Understanding Dividers and Glazing Bars
The Timber Cutting List editor has six loops which use similar logic:

Frame divider (full and partial) refers to any part added to the frame via the Transom / Mullion button.
Sash divider (full and partial) refers to any part added to the sash via the Transom / Mullion button, such as door muntins.
Glazing bar (full and partial) refers to any part added to the glazing via the GlazingBar button.
Full vs partial loops
The difference between full and partial loops is not whether the rule will trigger for a particular divider, but how many times the rule will trigger, and what values it will calculate for its visible_length_in_mm variable (sightline_length_in_mm for glazing bars).
With no other conditions in place, transoms and mullions will always trigger rules on the frame divider and partial frame divider loops, regardless of transom length. Thus a simple design like this will trigger identically on frame divider and partial frame divider loops:
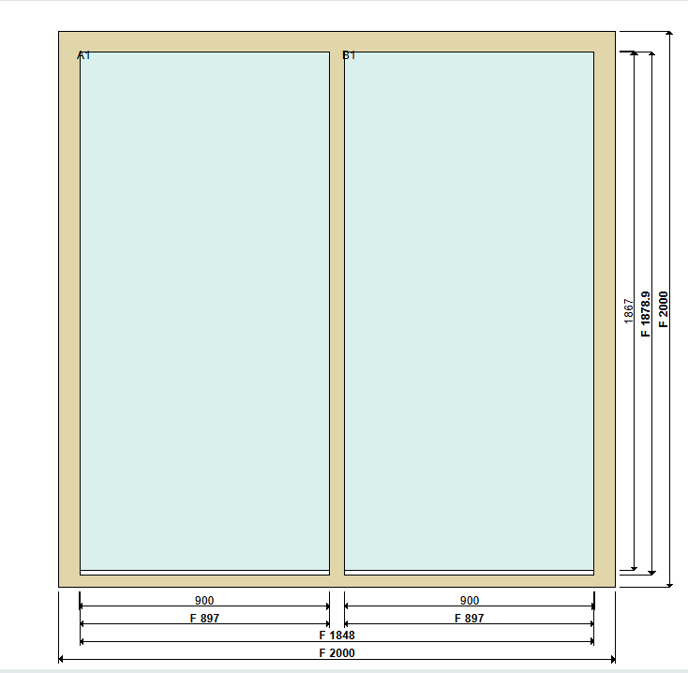
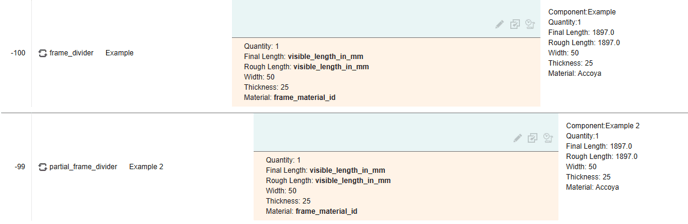
But when one divider intersects another, the loops behave differently. The frame divider loop considers the full length of each transom and mullion, whereas the partial frame divider loop considers the length up to the intersection:
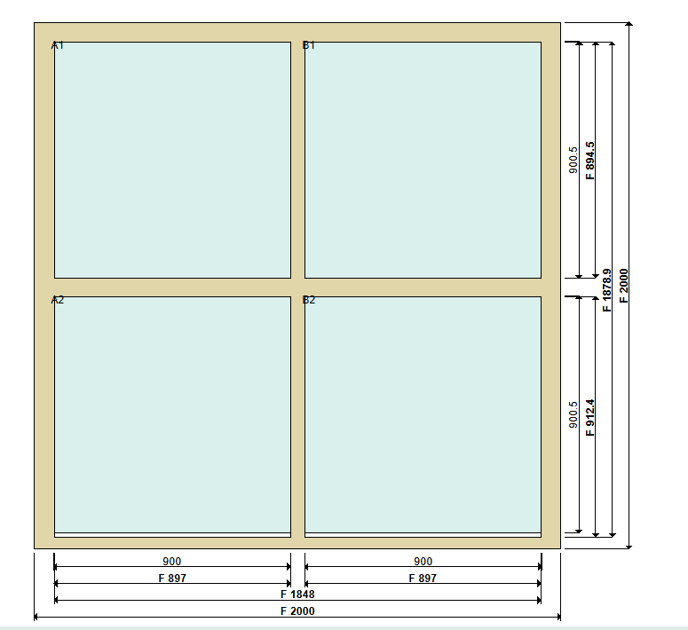
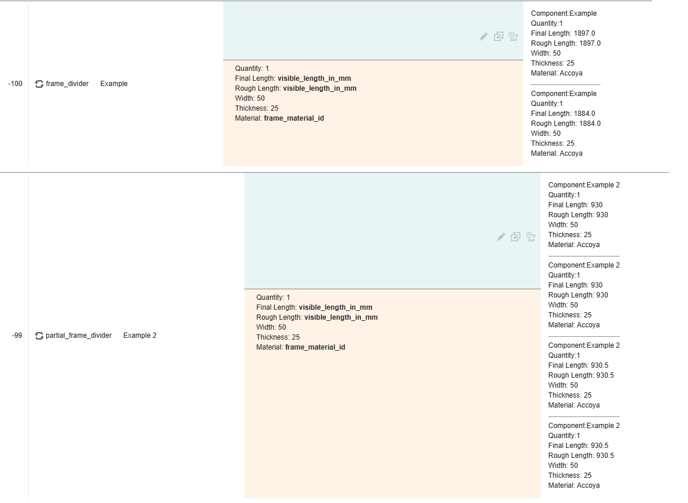
For the above drawing, the rule on the frame divider loop triggers twice, because the transom from jamb to jamb is considered as a single divider, as is the mullion from frame head to cill. On the partial frame divider loop the rule triggers four times, because this loops registers two mullions divided by a transom and two transoms divided by a mullion.
Tip: when writing TCL rules for transoms and mullions, put mullion rules on the frame divider loop, and transom rules on the partial frame divider loop, so that the above design would trigger as a single full-length mullion intersecting two separate transoms.
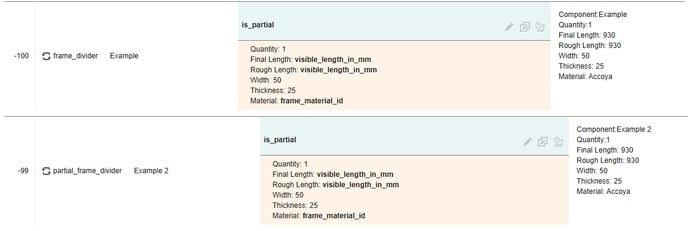
is_partial
The is_partial variable, which is available on full and partial loops, checks whether the divider is the full length of the frame/sash/glazing - it will only trigger if the divider stops when it reaches another divider, instead of continuing to the other end. The example below has a partial transom: 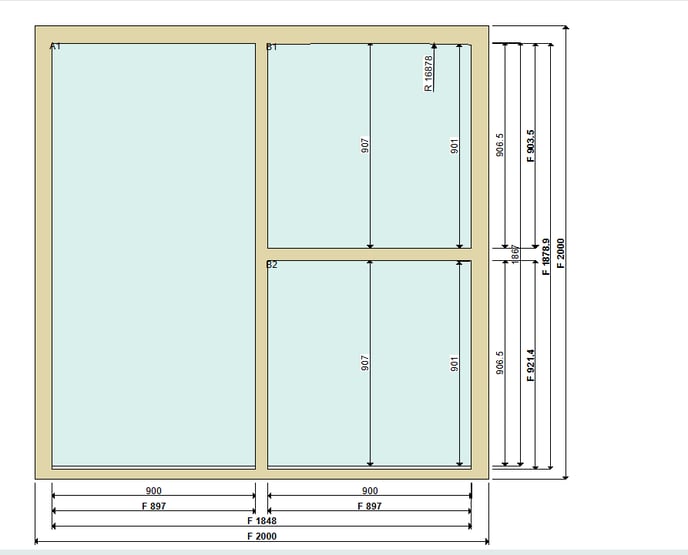
If we add this condition to our rules, they will only trigger for the partial transom, regardless of loop:
Sash dividers and glazing bars have exactly the same logic as frame dividers.